Exploring the Potential of Quantum Computing in Future CNC Machining
This blog explores the futuristic intersection of quantum computing and CNC machining—how it could revolutionize design simulation, process optimization, and real-time decision-making in manufacturing.

July 09, 2025
Share:
Introduction
The world of CNC machining is no stranger to innovation—from the rise of 5-axis machines to AI-powered automation and digital twins. But as we push the boundaries of speed, precision, and complexity, a new frontier is emerging on the tech horizon: quantum computing.
Though still in its early stages, quantum computing promises to revolutionize several industries by solving problems that are computationally impossible for classical computers. For the manufacturing world, particularly CNC machining, this could open new doors to real-time decision-making, ultra-efficient optimization, and highly accurate simulations.
In this blog, we’ll take a deep dive into how quantum computing could shape the future of CNC machining, even if we're just scratching the surface right now.
What is Quantum Computing—In Simple Terms?
Quantum computing is a new kind of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics. Unlike traditional computers that process data in bits (0 or 1), quantum computers use qubits—which can represent 0 and 1 at the same time through a property called superposition.
Add in entanglement and quantum tunneling, and you’ve got a machine that can solve incredibly complex problems at speeds that even supercomputers can’t match.
Now, how does that tie into CNC machining? Let’s find out.
Why CNC Machining Needs Quantum Help
Even the most advanced CNC systems today face some limitations:
- Optimizing tool paths in multi-axis machines can be extremely complex.
- Simulating thermal and mechanical stress takes time and computing power.
- AI-assisted CNC systems still rely on classical algorithms with bottlenecks.
- Real-time adjustments for mass customization are hard to scale.
These are precisely the types of challenges that quantum computers excel at tackling.
Potential Applications of Quantum Computing in CNC
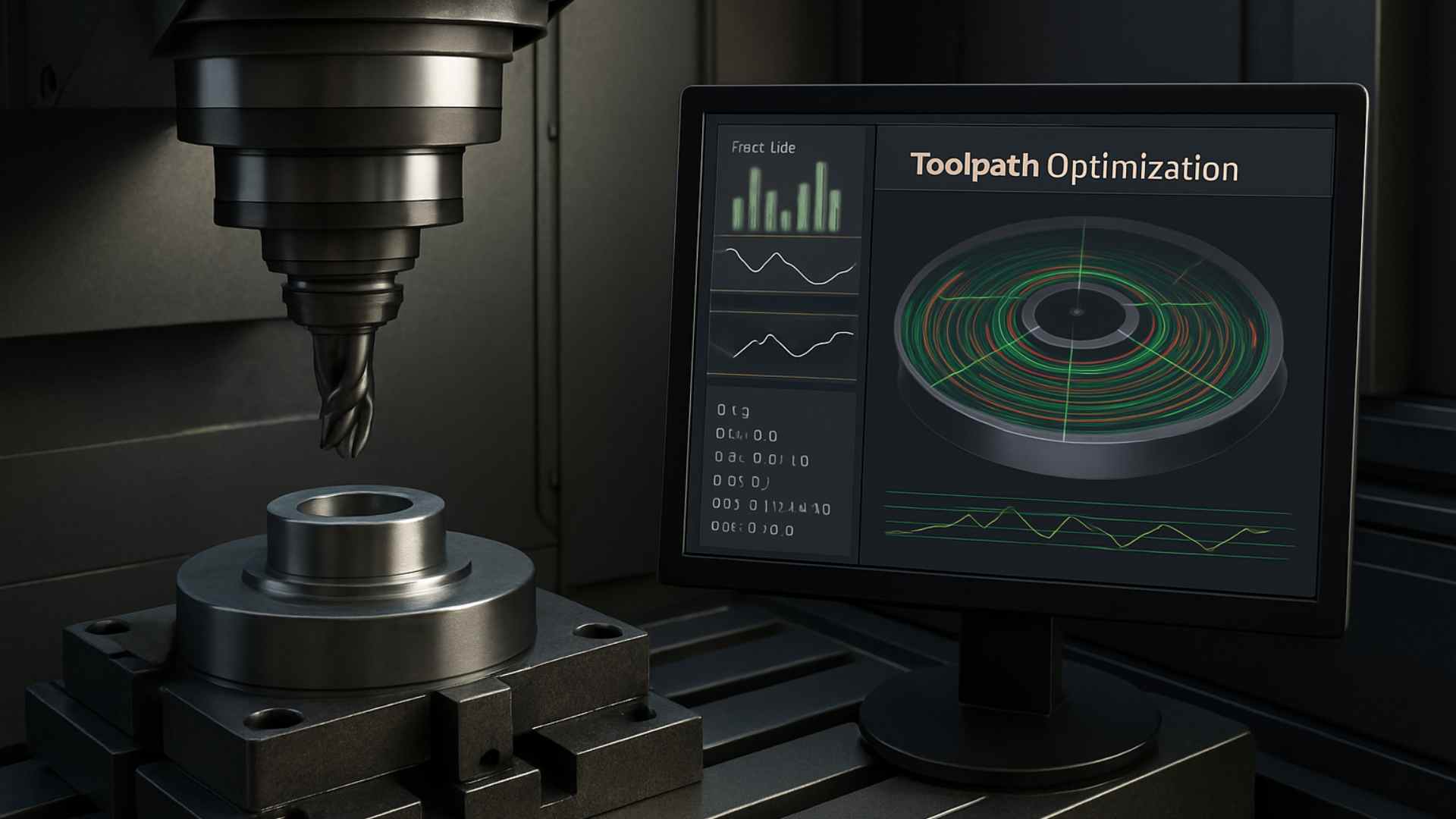
1. Toolpath Optimization at Unmatched Speed
One of the most computationally heavy tasks in CNC is determining the most efficient toolpath, especially in 5-axis or simultaneous machining.
With quantum algorithms, manufacturers could compute near-perfect paths instantly, reducing machine wear, cutting time, and energy use.
This would be particularly useful in high-volume production, mold machining, or parts requiring ultra-smooth surface finishes.
2. Quantum-Powered Simulation
Simulation is key in machining complex materials or parts. But simulating heat distribution, chip formation, or tool vibration requires serious processing power.
Quantum computing could drastically speed up:
- Material deformation predictions
- Thermal load simulations
- Real-time machine behavior modeling
3. Next-Level Predictive Maintenance
Machine downtime is costly. While current systems use sensors and AI to predict failures, quantum computing can:
- Analyze exponentially more sensor data in real time
- Detect complex failure patterns
- Optimize maintenance schedules based on millions of variables
This means smarter maintenance, fewer breakdowns, and longer machine lifespans.
4. Real-Time Customization at Scale
In industries where customization is key (like medical implants or aerospace parts), the ability to optimize each part's machining strategy on-the-fly is a game changer.
Quantum computers can instantly calculate the best parameters for:
- Speed/feed combinations
- Cutting strategies
- Finishing processes
This would make mass customization truly scalable—something classical computing still struggles with.
5. Smarter AI Models for CNC
AI is already playing a growing role in CNC automation, but most models today run on classical hardware.
Quantum AI could enhance:
- Decision-making models for adaptive machining
- Automated error correction during operation
- Design-to-manufacture optimization tools
Current Limitations and Barriers
It’s important to acknowledge that we’re not there yet:
- Quantum hardware is still in development.
- Qubits are extremely fragile and sensitive.
- Most quantum systems need cryogenic environments to operate.
- Integrating quantum computing into factory floors is a long-term goal.
So, for now, quantum computing is more of a "when" than an "if."
But early-stage collaborations between tech companies and manufacturers are already in motion. Think of it like how AI was in the early 2000s—soon to become a must-have.
Quantum + CNC: A Future Scenario
Let’s imagine a future shop floor:
A designer uploads a complex part file. A hybrid classical-quantum system instantly analyzes stress points, determines the best material, generates the most efficient toolpaths, simulates heat distribution, and sends real-time instructions to the CNC machine—all in under 30 seconds.
If mid-process anomalies occur, quantum-enhanced AI predicts and corrects them on the spot, ensuring zero-defect manufacturing.
Science fiction? Not for long.
Conclusion
Quantum computing may sound futuristic, but its implications for CNC machining are real and exciting. From smarter optimization and hyper-accurate simulations to predictive maintenance and real-time customization, quantum tech holds the potential to reshape manufacturing as we know it.
While we might not see full integration tomorrow, forward-looking manufacturers and software developers are already laying the groundwork. Staying informed and ready could mean gaining a serious edge in the not-so-distant future of CNC machining.
Explore More from Sahil Machines
FAQ
Quantum computing is still in the research and early commercialization stage. Realistic, large-scale industrial use may take another 5–10 years, but early adopters are already exploring pilot programs.
No, most quantum computing applications will likely be delivered through cloud platforms, not local machines. CNC software vendors may eventually offer quantum-enhanced modules.
Not replace, but complement. It will likely work alongside traditional software to boost performance in high-complexity tasks.
While it’s expensive today, future Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models could make quantum capabilities accessible and affordable even for small shops.
Yes. IBM, Google, and Honeywell are investing heavily in quantum computing. Siemens and Dassault Systèmes are also exploring quantum-enhanced simulation for manufacturing.
Follow Us:
Latest Posts
Get in touch with us about anything.
Connect with our team to explore the alloy solutions and machinery expertise you need.